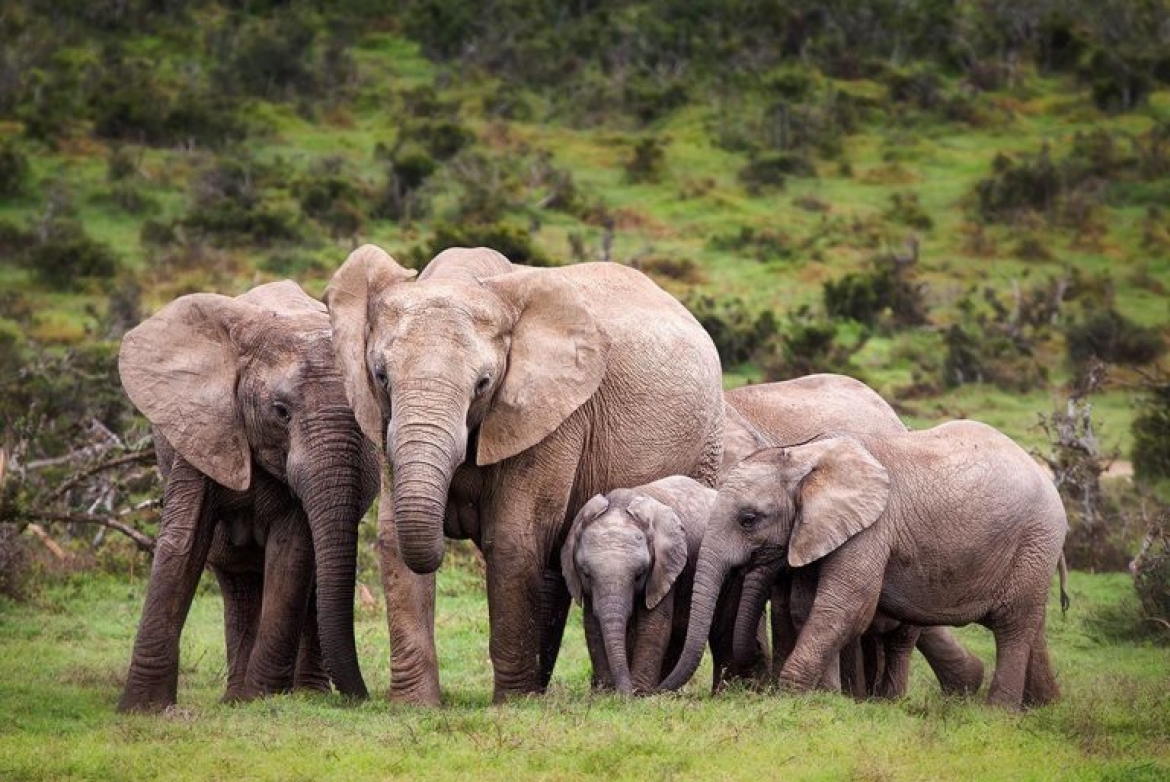
Kafta-Shiraro is located in western Tigray, With its 500,000 ha area, it is one of the largest conservation areas in Ethiopia. It is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Shiraro in the east, Wolkaite in the south and Humera in the west. Within Tigray it is positioned in the woredas of Kafta-Humera and Tahtay-Adiabo. While the main river is the Tackazee, it is fed by a number of riverst that orginate in the Simen Mountains and highlands of Wolkait. Elevation ranges from 550 masl on the edge of Tackaze River 1800 masl on the highlands of Kafta. The agro-climatic zone is identified as Qolla with an inclination to semi-arid. Vegetation communities within the reserve include Acacia-Commiphora,combretum-Terminalia, dry evergreen montane woodlands and riparian types. The site has a mono-modal pattern of rain with high peaks in May and early September. Preliminary records show that the site conserves 42 mammalian and 95 avian species. Major wildlife conserved include Ostrich, Aardvark, Elephant, Greater kudu, Roan Antelope, Red-fronted Gazelle, Caracal, Leopard and Lion.
Unique features - The reserve is important for the conservation of Elephants. It is one of nine sites in Ethiopia that conserve Elephants. The Elephant population in Kafta migrates seasonally between Ethiopia and Eritrea. At present the site is known to hold an estimated 100-150 individual Elephants. Besides Elephants, it conserves 42 mammals 167 birds and 9 reptile species. The site is extremely important and could well be the only site in the country for wintering Demoiselle Crane. A recent discovery shows that the northwestern border of the park holds more than 20,000 Demoiselle Cranes.